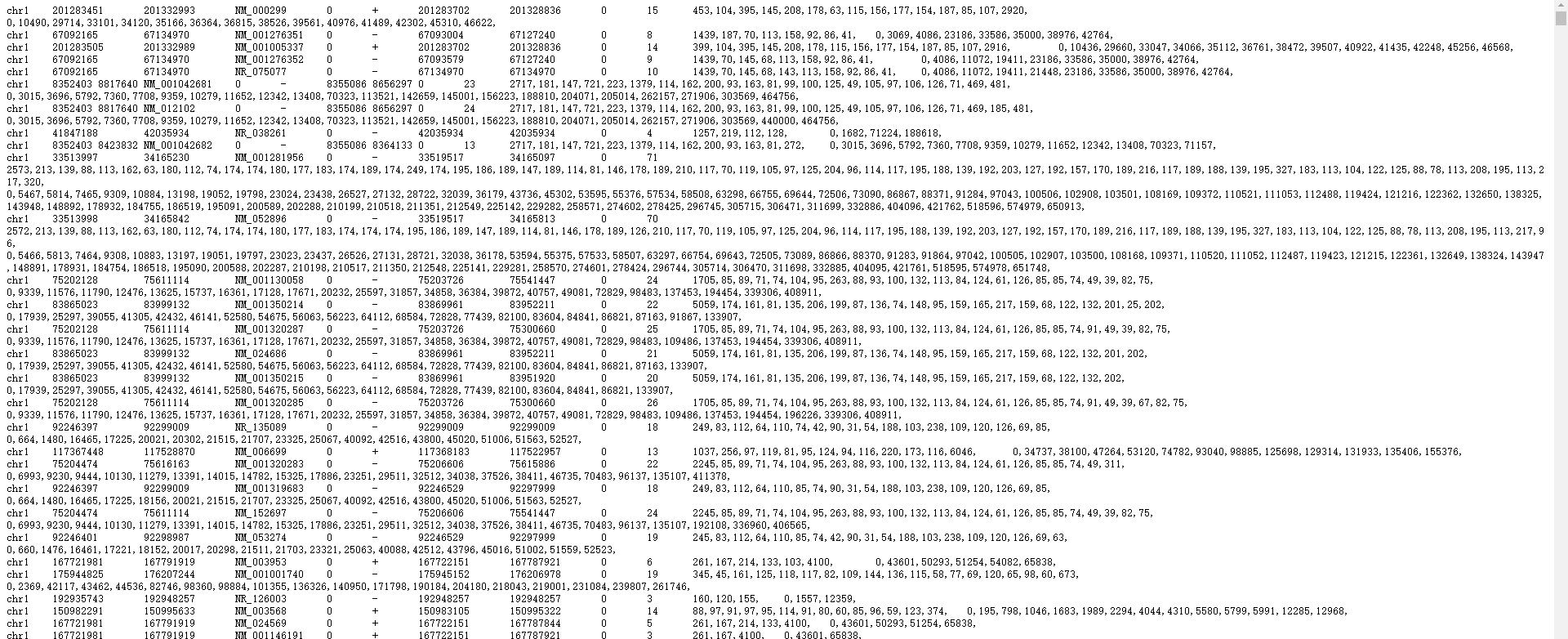
为deepTools的computeMatrix创建gene.bed文件
我们在使用deepTools的computeMatrix命令时,常见的使用方法如下:
An example usage is:
computeMatrix scale-regions -S <biwig file(s)> -R <bed file> -b 1000
此处的--regionsFileName, -R指的是bed文件,bed文件是指示interest region的文件,而当你需要从全基因组范围上查看bw文件的信号强度的时候,就需要获得类似于hg19.bed之类的提取出所有transcript的bed file,面对这种需求的时候,我们一般可以有以下两种方法:
- 从对应物种的GTF文件中提取出gene/transcript对应的chr-start-end信息,写入到bed文件里即可
- 从UCSC的Table Browser中进行提取
GTF pathway(Linux)
1. Script
2. 通过GTF文件写简单的处理脚本获得(举例,不是对应代码)
转换GTF文件到bed文件实例:
head -n 1 Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.90.gtf
#!genome-build GRCh38.p10
#!genome-version GRCh38
#!genome-date 2013-12
#!genome-build-accession NCBI:GCA_000001405.25
#!genebuild-last-updated 2017-06
1 havana gene 11869 14409 . + . gene_id "ENSG00000223972"; gene_version "5"; gene_name "DDX11L1"; gene_source "havana"; gene_biotype "transcribed_unprocessed_pseudogene";
awk -vb=chr -F '[\t ;"]' '$3 == "gene"{print b$1,$4,$5,$21}' OFS="\t" Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.90.gtf > GRCh38.bed
head -n 1 GRCh38.bed
chr1 11869 14409 ENSG0000022397
UCSC pathway(以human的gene.bed举例)
首先打开table browser网页:
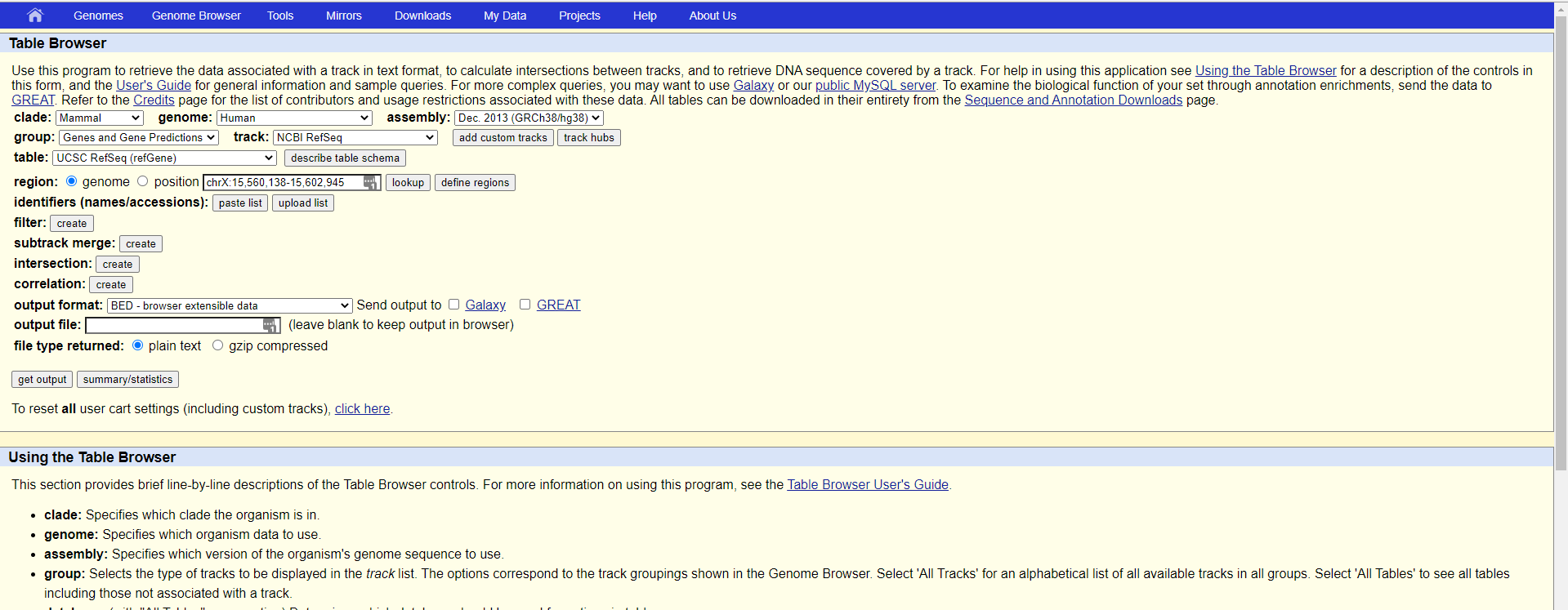
这里我们需要的注意的是以下几个选项:
支系(Clade):以人为例的话,就该选Manmal哺乳动物,如果要看斑马鱼,就得到Vertebrate里面去看了
物种基因组(genome):这个选框就对应你要直接看的研究对象了,我们这里还是以human为例
版本(assembly):这里需要注意的是,需要选取你比对的参考基因组的版本,不然基因位置会变化
需求信息(group):也就是你需要拿到哪些column的信息,我们这里需求的是基因转录本信息,所以选择Genes and Gene Predictions
数据库(track):等于选取你需要使用的数据库,我们这里选取最常用的NCBI的refseq版本就可以
展示类别(table):在这里你可以选择是否需要展示所有信息还是部分需求数据即可,我们这里选择UCSC RefSeq
- 关于table选项的一些释义:
- RefSeq All – all curated and predicted annotations provided by RefSeq.
- RefSeq Curated – subset of RefSeq All that includes only those annotations whose accessions begin with NM, NR, NP or YP. (NP and YP are used only for protein-coding genes on the mitochondrion; YP is used for human only.)
- RefSeq Predicted – subset of RefSeq All that includes those annotations whose accessions begin with XM or XR.
- RefSeq Other – all other annotations produced by the RefSeq group that do not fit the requirements for inclusion in the RefSeq Curated or the RefSeq Predicted tracks.
- RefSeq Alignments – alignments of RefSeq RNAs to the human genome provided by the RefSeq group, following the display conventions for PSL tracks.
- RefSeq Diffs – alignment differences between the human reference genome(s) and RefSeq transcripts. (Track not currently available for every assembly.)
- UCSC RefSeq – annotations generated from UCSC’s realignment of RNAs with NM and NR accessions to the human genome. This track was previously known as the “RefSeq Genes” track.
- RefSeq Select+MANE (subset) – Subset of RefSeq Curated, transcripts marked as RefSeq Select or MANE Select. A single Select transcript is chosen as representative for each protein-coding gene. This track includes transcripts categorized as MANE, which are further agreed upon as representative by both NCBI RefSeq and Ensembl/GENCODE, and have a 100% identical match to a transcript in the Ensembl annotation. See NCBI RefSeq Select. Note that we provide a separate track, MANE (hg38), which contains only the MANE transcripts.
- RefSeq HGMD (subset) – Subset of RefSeq Curated, transcripts annotated by the Human Gene Mutation Database. This track is only available on the human genomes hg19 and hg38. It is the most restricted RefSeq subset, targeting clinical diagnostics.
附上释义原文:
clade: Specifies which clade the organism is in.
genome: Specifies which organism data to use.
assembly: Specifies which version of the organism’s genome sequence to use.
group: Selects the type of tracks to be displayed in the track list. The options correspond to the track groupings shown in the Genome Browser. Select ‘All Tracks’ for an alphabetical list of all available tracks in all groups. Select ‘All Tables’ to see all tables including those not associated with a track.
database: (with “All Tables” group option) Determines which database should be used for options in table menu.
track: Selects the annotation track data to work with. This list displays all tracks belonging to the group specified in the group list. Some tracks are not available when the region is set to genome due to the data provider’s restrictions on sharing.
table: Selects the SQL table data to use. This list shows all tables associated with the track specified in the track list. Some tables may be unavailable due to the data provider’s restrictions on sharing.
describe table schema: Displays schema information for the tables associated with the selected track.
region: Restricts the query to a particular chromosome or region. Select genome to apply the query to the entire genome (not available for certain tracks with restrictions on data sharing). In some Human assemblies, you may select ENCODE to examine only the ENCODE Pilot regions. To limit the query to a specific position, type a chromosome name, e.g. chrX, or a chromosome coordinate range, such as chrX:100000-200000, or a gene name or other id in the text box. You can select multiple genomic regions by clicking the “define regions” button and entering up to 1,000 regions in a 3- or 4-field BED file format.
lookup: Press this button after typing in a gene name or other id in the position text box to look up the chromosome position
identifiers (selected tracks only): Restricts the output to table data that match a list of identifiers, for instance RefSeq accessions for the RefSeq track. If no identifiers are entered, all table data within the specified region will be displayed.
filter: Restricts the query to only those items that match certain criteria, e.g. genes with a single exon. Click the Create button to add a filter, the Edit button to modify an existing filter, or the Clear button to remove an existing filter.
intersection (selected tracks only): Combines the output of two queries into a single set of data based on specific join criteria. For example, this can be used to find all SNPs that intersect with RefSeq coding regions. The intersection can be configured to retain the existing alignment structure of the table with a specified amount of overlap, or discard the structure in favor of a simple list of position ranges using a base-pair intersection or union of the two data sets. The button functionalities are similar to those of the filter option.
output:
Specifies the output format (not all options are available for some tracks). Formats include:
- all fields from selected table - data from the selected table displayed in a tab-separated format suitable for import into spreadsheets and relational databases. The ASCII format may be read in any web browser or text editor.
- selected fields from primary and related tables - user-selected set of tab-separated fields from the selected table and (optionally) other related tables as well.
- sequence - DNA (or protein sequence, in some cases) associated with the table.
- BED - positions of data items in a standard UCSC Browser format with the name column containing exon information separated by underscores.
- GTF - positions of all data items in a limited gene transfer format (both BED and GTF formats can be used as the basis for custom tracks).
- CDS FASTA alignment from multiple alignment - FASTA alignments of the CDS regions of a gene prediction track using any of the multiple alignment tracks for the current database. Output sequence can be in either nucleotide-space or translated to protein-space. Available only for genePred tracks.
- custom track - customized Genome Browser annotation track based on the results of the query.
- hyperlinks to Genome Browser - returns a page full of hyperlinks to the UCSC Genome Browser, one for each item in the table.
- data points - the data points that make up a graph (aka wiggle) track.
- MAF - multiple alignments in MAF format
Send output to Galaxy: displays results of query in Galaxy, a framework for interactive genome analysis.
Send output to GREAT: displays the functional enrichments of the query results in GREAT, a tool for analysis of the biological function of cis-regulatory regions.
file type returned:
When a filename is entered in the “output file” text box, specifies the format of the output file:
- plain text - data is in ASCII format
- gzip compressed - data is compressed in gzip format
get output: Submits a data query based on the specified parameters and returns the output.
summary/statistics: Displays statistics about the data specified by the parameters.
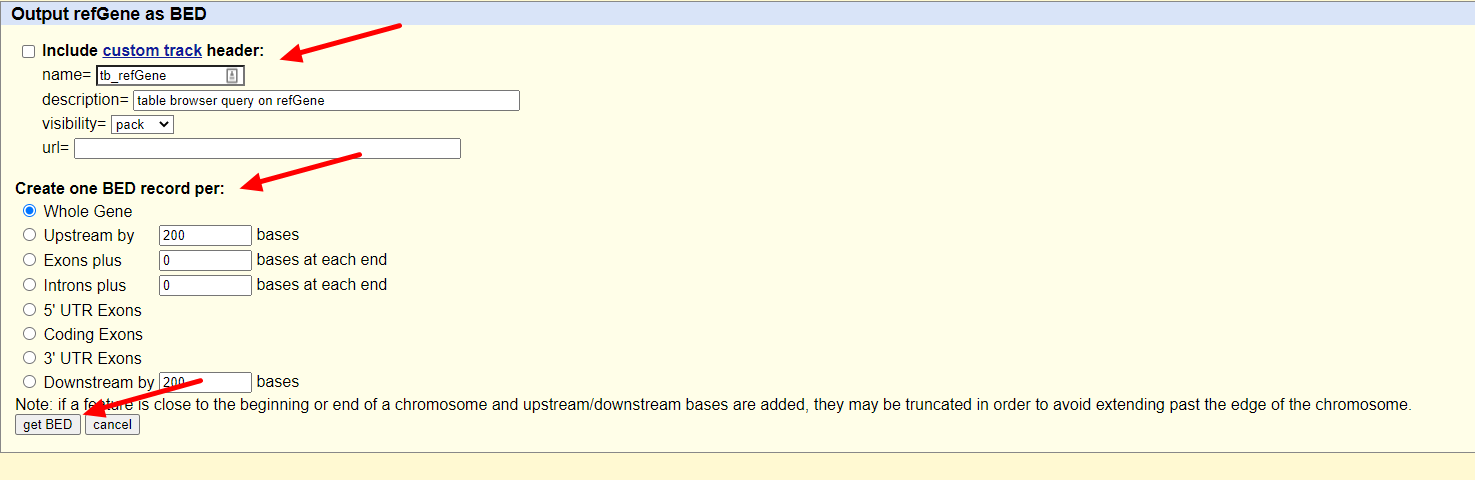
随后我们只需要在output format一栏选择BED文件格式就可以了,保持其余的选项不动,点击get output按钮:
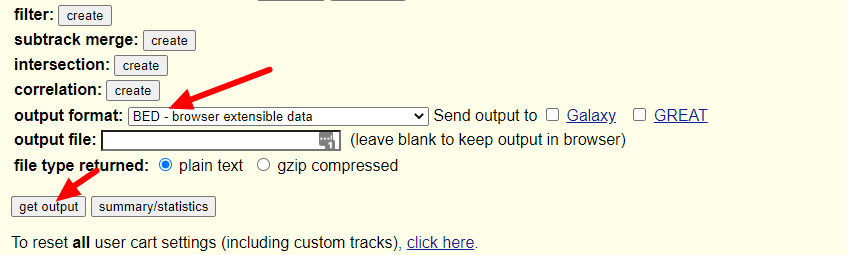
随后跳出的界面会让我们选择是否包含header,以及是否需要往两侧延申bed文件记录的基因位置(当然是不需要啦),继续点击get output:
dada,我们就拿到我们需要的gene.bed文件啦,另存为文件即可: